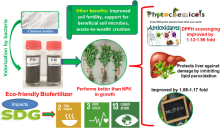
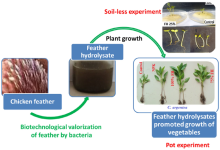
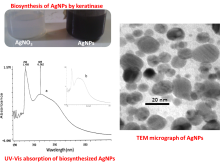
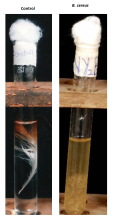
In 2023, we showed that feather hydrolysates promoted the growth of vegetables on the field and improved their functional properties........
The present study reports the application of feather hydrolysates (FHs) obtained from the hydrolysis of chicken feathers by Bacillus safensis LAU 13 (KJ461434) and Aquamicrobium defluvii FH 20 (OM281847.1) as organic nitrogen fertilizer for the cultivation of Corchorus olitorius, Celosia argentea and Amaranthus caudatus